About disease
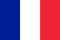
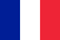
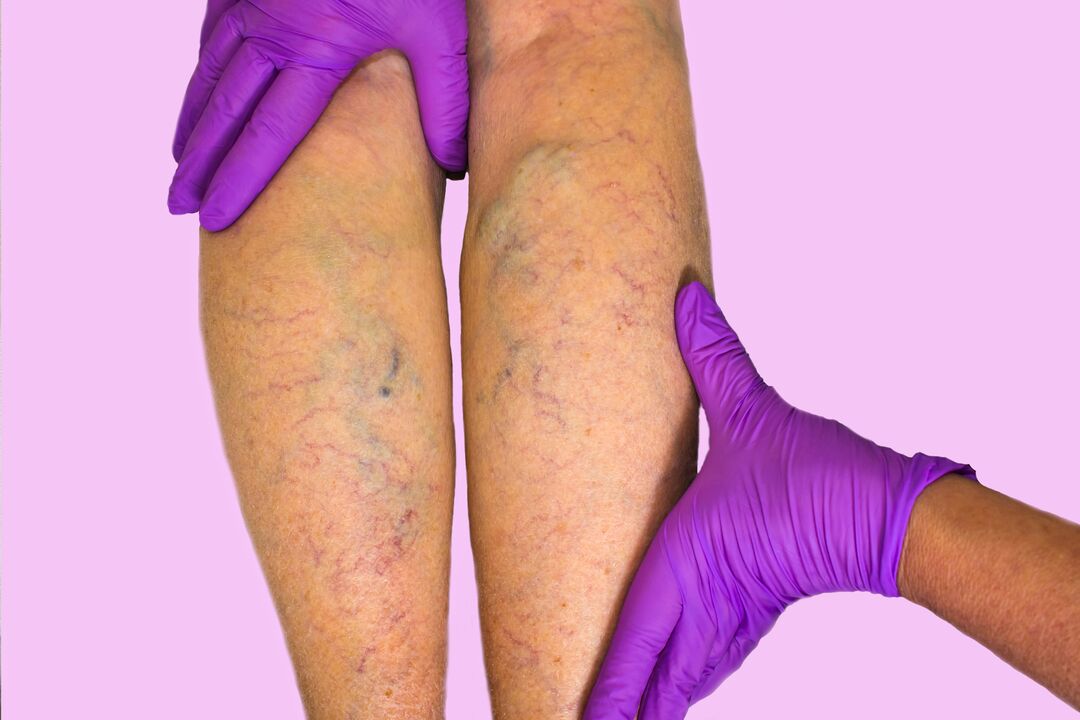
Types of varicose veins
- Rectal varicose veins (hemorrhoids);
- esophageal vein dilatation;
- Varicocele (varicocele) in men;
- Varicose veins of lower limbs.
- C0 - no sign;
- C1 - the appearance of varicose veins and stellate veins;
- C2 - varicose veins;
- C3 – Swelling in the legs, indicating venous insufficiency;
- C4 – Nutritional changes in the form of hyperpigmentation, lipodermatosclerosis (thickening of the skin on the lower third of the legs);
- C5 – Heals venous ulcers;
- C6 – Non-healing venous ulcer.
symptom
- Heaviness and swelling in the legs (calves), worsening at night;
- increased leg fatigue;
- Soreness in the lower legs that occurs after remaining in a stationary position, standing, or sitting for an extended period of time.
Causes of varicose veins
- Genetics: In most cases, varicose veins are caused by mutations in the genes responsible for the structure of the valves and walls of the veins;
- being overweight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- Increased load on the venous system of the extremities due to standing work;
- Pregnancy and childbirth, menopause, hormonal imbalances.
diagnosis
- Ultrasound duplex scanning. Allows you to assess the condition of the valves, the strength and direction of blood flow, the size of the blood vessels, and determine whether blood clots are present.
- Valve function studies: compression testing, simulated walking, Paraná maneuver.
- X-ray contrast venography is an X-ray examination in which contrast material is injected into a vein. Helps assess valve function, venous patency and detect blood clots.
Expert opinion
- Nutritional disorders. The appearance of large, brown spots on the legs or thighs, followed by the formation of large, non-healing ulcers that are itchy and painful.
- Thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of the vein wall with the deposition of clots in the vein wall. Thrombus veins become red, thickened, painful, and the surrounding temperature increases. In appearance, it resembles an abscess. Threatens the spread of infection throughout the body.
- bleed. Bleeding from ruptured dilated veins can occur both inside and outside the tissue. The bleeding was severe and an ambulance needed to be called.
- Thromboembolism. Blood clots that form in dilated veins can rupture and block important arteries, such as the pulmonary artery. This condition usually results in immediate death.
Treatment of varicose veins
- Compression therapy - Wearing Type A and Type I support knitwear (socks, tights) to prevent backflow of blood.
- Medication - Intravenous medications are given to increase venous tone. These treatments will not eliminate external symptoms, but they will eliminate subjective symptoms such as heaviness, swelling, and soreness.
- Phlebosclerosis occurs when a hardening substance is introduced into small blood vessels, gluing them together. Microsclerotherapy frees you from the network of blood vessels.
- Laser Therapy – can eliminate the tiny imperfections that remain after microsclerotherapy. During the procedure, the doctor shines a beam of light onto the affected area.
prevention
- Minimize static load on the legs;
- Eat properly and, if necessary, take intravenous supplements as prescribed by your doctor;
- Wear compression stockings when standing for long periods of time.